Type 1 Diabetes: Next Steps After Your Child's Diagnosis
Diabetes is a disease that changes how the body uses glucose (sugar). Glucose comes from food and is the major fuel for our bodies. When we eat, glucose moves from the digestive system (stomach and intestines) into the bloodstream. A hormone called insulin helps the glucose move from the bloodstream into our cells, giving energy to our bodies. When the body doesn't have insulin, glucose stays in the bloodstream.
Finding out that your child has diabetes can be upsetting. The diabetes health care team is here to help your child and your whole family.
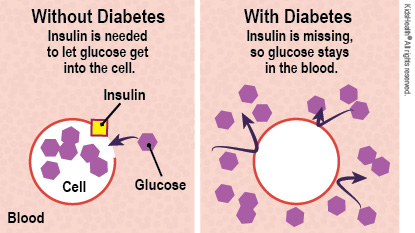


Why doesn't my child's body have insulin? There is no insulin in your child's body because the pancreas that usually makes insulin no longer makes it. Without insulin, the level of glucose in the blood rises too high. High blood glucose levels (also called blood sugar levels) can cause a number of health problems.
Can type 1 diabetes be prevented? No, type 1 diabetes can't be prevented. Nothing that either a parent or the child did caused the disease. Type 1 diabetes does not go away and requires lifelong treatment with insulin.
What are the early symptoms of type 1 diabetes? Early symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually include:
How can I help my child with diabetes? You can help your child live a happy, healthy life by learning more about diabetes and encouraging your child to eat well, exercise, and stay on top of blood sugar control every day.