Type 2 Diabetes: How to Care for Your Child
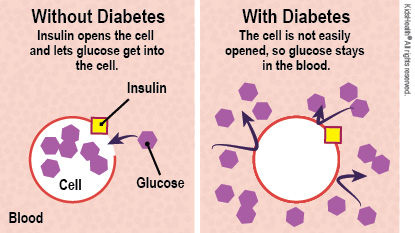
Type 2 diabetes happens when the body cannot use or make enough insulin. It is a permanent problem. But healthy eating, exercise, and medicine can help keep your child's glucose (blood sugar) under control. In a person with type 2 diabetes, blood sugar doesn't get into the cells easily and can't give energy to the body. This is called insulin resistance. Insulin resistance raises the blood sugar level. This makes the pancreas work harder to make more insulin.

-
Give your child any prescribed medicines as directed.
-
Your child should eat a healthy, well-balanced diet.
-
Make sure your child follows the food guidelines recommended by the health care provider or diabetes dietitian.
-
Encourage your child to get regular exercise. It helps improve the body's response to insulin.
-
It's important to check blood sugar levels on schedule. If levels are too high or too low, follow your health care provider's instructions for getting them back in the target range.
-
Schedule regular checkups to make sure the treatment plan is working.

Your child:
-
has very low blood sugar that doesn't go back up with home treatment
-
has fast, deep breathing or trouble breathing
-
appears dehydrated; signs include dizziness, drowsiness, a dry or sticky mouth, sunken eyes, less pee or darker than usual pee, crying with little or no tears
-
is confused or loses consciousness
-
has continued vomiting or severe belly pain

How does a person get type 2 diabetes? It's not known for sure how people get type 2 diabetes. But risk factors include:
-
Many kids with type 2 diabetes have at least one parent with diabetes and a family history of it. So there seems to be a genetic risk.
-
Being overweight makes a person insulin-resistant and more likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
-
Kids in puberty are more likely to have it than younger kids. This is probably because normal increases in hormone levels during fast growth and physical development can cause insulin resistance.
What is the treatment for type 2 diabetes? The treatment plan usually includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, and, often, medicine that improves how the body responds to insulin. Some kids may need insulin too, given by shots or through an insulin pump.