Uncontrolled Type 1 Diabetes: How to Care for Your Child
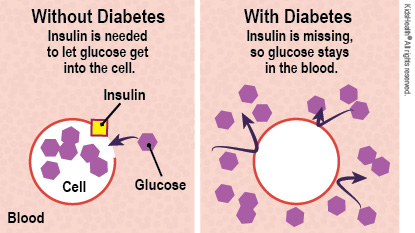
Getting control of blood sugar levels can help prevent serious health problems. Your child's diabetes is not well controlled. A blood test, called HbA1c, showed that your child's blood sugar has not been under control for the past 2 to 3 months. Uncontrolled blood sugar can be caused by:
-
not testing blood glucose levels regularly
-
skipping insulin shots
-
eating too many carbohydrates for the amount of insulin given
-
not changing the diabetes treatment plan when there's a change in physical activity or when your child is sick
-
mechanical problems with an insulin pump, if your child uses one
To protect your child's health, it's important to keep blood sugar under control each and every day.

-
Check blood glucose levels several times a day. Change insulin doses, food, and exercise based on the readings.
-
Make sure an adult watches when your child checks blood sugar levels or injects insulin.
-
If your child has an insulin pump, check the pump and infusion catheter regularly to make sure they're working correctly.
-
When your child is sick, check blood sugar levels often. Also check your child's urine (pee) for ketones as you were shown by the diabetes team.

-
Blood sugar levels are often high or low based on what the diabetes care team told you.
-
Your testing shows ketones in your child's urine.
-
Your child isn't eating or drinking as expected.
-
Your child has vomiting or diarrhea.
Your child:
-
has ongoing nausea, vomiting, or belly pain
-
has fast, deep breathing or trouble breathing
-
appears dehydrated; signs include dizziness, drowsiness, a dry or sticky mouth, sunken eyes, crying with few or no tears, dark pee, or peeing less often

How can my child avoid uncontrolled diabetes in the future? Your child should:
-
Check blood sugar levels a few times a day by testing a small blood sample.
-
Give themselves insulin injections, have an adult give them injections, or use an insulin pump.
-
Get regular exercise to help control blood sugar levels.
-
Eat a healthy diet and pay special attention to the amounts of sugars and starches.
-
Eat meals at regular times, if possible.
-
Stay in close contact with their health care provider and diabetes health care team to get the best possible diabetes control.
What is the HbA1c test? The HbA1c test is a blood test that can show if your child's glucose has been out of control. It measures the amount of glucose attached to hemoglobin (a protein in the blood). The hemoglobin test (HbA1C for short) gives information about blood glucose control in the 2 to 3 months before the test. This lets health care providers know if the diabetes care plan needs changes.